Beginning with Hyper-V on Windows 2008 Snapshots made their appearance. Later on, on Windows Server 2012 R2 snapshots were renamed in Checkpoints but yet the functionality remained the same. What is an actual Checkpoint? A Checkpoint is a point in time image of a virtual machine that we could easily revert back. Not recommended for production workloads though (only for Test / Dev scenarios) because it is not reliable due to the way that operates by design (captures memory state) and may lead to data corruption.
Now with Hyper-V 2016 a new type of Checkpoints has been introduced, Production Checkpoints! It utilizes the VSS Writers (Windows Guests) or file system freeze (Linux Guests) to provide the ability for the applications to cease all I/O operations and flush data from memory to disk in order to create a data-consistent backup of the virtual machine. Integration Services must be enabled for the underlying Virtual Guests (mandatory!).
In Hyper-V 2016, Production Checkpoints are enabled by default but with an option to choose the old Standard Checkpoints instead.
Changing the Checkpoint Type
Using Hyper-V Manager
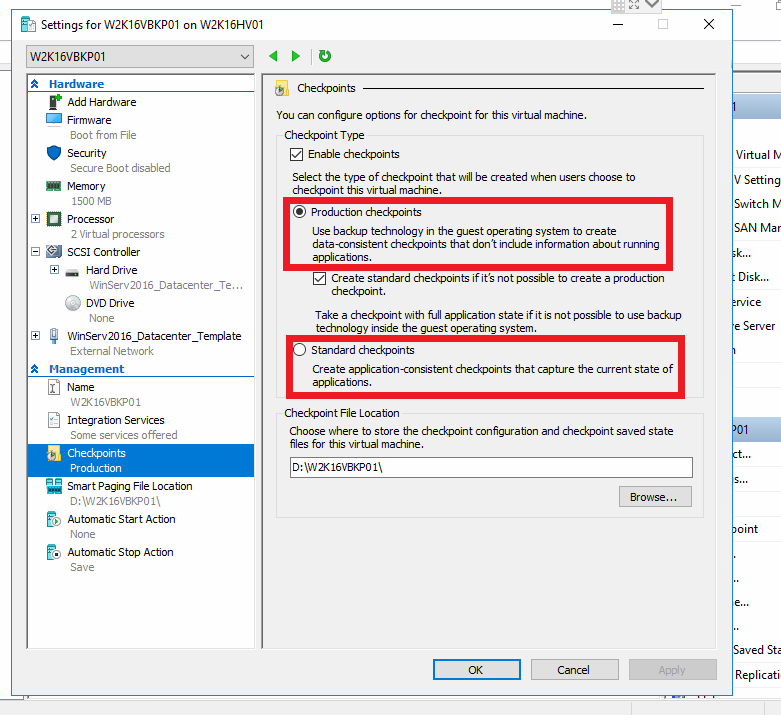
- Open Hyper-V Manager.
- Right click on a virtual machine and select Settings.
- Under Management select Checkpoints.
- Select the desired checkpoint type.
Using PowerShell
- Set to Standard Checkpoint:
Set-VM -Name <vmname> -CheckpointType Standard
- Set to Production Checkpoint, if the production checkpoint fails a standard checkpoint is being created:
Set-VM -Name <vmname> -CheckpointType Production
- Set to Production Checkpoint, if the production checkpoint fails a standard checkpoint is not being created.
Set-VM -Name <vmname> -CheckpointType ProductionOnly
More posts on Windows Server 2016 Virtualization:

You must be logged in to post a comment.